Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearing
Single direction angular contact thrust ball bearings
Single direction angular contact ball bearings (fig 1) are able to take up axial loads acting in one direction. They are of separable design, i.e. the washers and ball and cage assembly can be mounted individually. In the main application area for these bearings – rotary tables – two bearings are always adjusted against each other. The second bearing has to carry the weight of the drill when it is stationary and has a higher load load carrying capacity than the first bearing.
Double direction angular contact thrust ball bearings
In bearings of the double direction design (fig 2), the upper bearing with the higher load carrying capacity and the smaller bearing which locates in the opposite direction are combined togther to form a unit. These bearings have low height and can accommodate axial loads acting in both directions as well as moment loads. A single bearing can therefore be used to support rotating machine components in relation to stationary components. These double direction bearings are also of separable design.
In addition to the angular contact thrust ball bearings described here, SKF also manufactures single direction bearings – screw support bearings (fig 3)
– and double direction precision bearings for the work spindles of machine tools (fig 4
Misalignment
Angular contact thrust ball bearings cannot tolerate any misalignment of the shaft with respect to the housing or any angular misalignment of the support surfaces on the shaft and in the housing.
Cages
Angular contact thrust ball bearings are produced either with a full complement of balls (without cage) or are fitted with machined brass cages (fig 6) which are centred on the shaft washer or the housing washer
Minimum load
When angular contact thrust ball bearings operate at high speeds, the centrifugal forces and gyratory moments acting on the balls may cause them to slide on the raceways. To prevent the damaging consequences of this, for example smearing, the bearing must always be subjected to a given axial load.
The requisite minimum axial load to be applied to single direction angular contact thrust ball bearings can be obtained from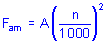
where
Fam =minimum axial load, kN
A= minimum load factor (see product tables)
n = rotational speed, r/min
When starting up at low temperatures or when the lubricant is highly viscous, even greater loads may be required. The weights of the components supported by the bearing, together with the external forces, generally exceed the requisite minimum load. The double direction angular contact ball bearings are preloaded by adjusting the two shaft washers against each other.
Equivalent dynamic bearing load
For single direction angular contact thrust ball bearings
P = Fa when Fa/Fr ≤ e
P = Fa + XFr when Fa/Fr > e
The values of factors e and X will be found in the product tables.
Equivalent static bearing load
For single direction angular contact thrust ball bearings
P0 = Fa + X0Fr
The values of factor X0 will be found in the product tables.







Comments